

These sensations are known as palpitations. You may also have the sensation that your heart is skipping a beat, fluttering, or beating too hard. If your heart rate climbs higher or drops lower, this may be a sign of an irregular heartbeat. The average heart rate for a healthy person over age 10 is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. The ECG in Acute MI.What’s the difference between a healthy and irregular heartbeat? An irregular heartbeat may be too fast, too slow, or inconsistent. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004 ECG’s for the Emergency Physician Part I 1e, 2003 and Part II Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008 Critical Decisions in Emergency and Acute Care Electrocardiography 1e, 2009 Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021 Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. ECG Mastery: Blue Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Different Patterns of Interatrial Conduction in Clockwise and Counterclockwise Atrial Flutter. Studies in man after open heart surgery using fixed atrial electrodes. Wells JL Jr, MacLean WA, James TN, Waldo AL.A classification of atrial flutter and regular atrial tachycardia according to electrophysiological mechanisms and anatomical bases a Statement from a Joint Expert Group from The Working Group of Arrhythmias of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Saoudi N, Cosío F, Waldo A, Chen SA, Iesaka Y, Lesh M, Saksena S, Salerno J, Schoels W Working Group of Arrhythmias of the European of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology.Rob Orman ERCast – Atrial Flutter, Fibrillation and Ablation (podcast).In contrast, atrial fibrillation will be completely irregular, with no patterns to be discerned within the R-R intervals.Look for identical R-R intervals occurring sporadically along the rhythm strip then look to see whether there is a mathematical relationship between the various R-R intervals on the ECG.assuming an atrial rate of 300bpm (P-P interval of 200 ms), the R-R interval would be 400 ms with 2:1 block, 600 ms with 3:1 block, and 800 ms with 4:1 block In atrial flutter with variable block the R-R intervals will be multiples of the P-P interval - e.g.Atrial flutter will not usually cardiovert with these techniques (unlike AVNRT), although typically there will be a transient period of increased AV block during which flutter waves may be unmasked.Turn the ECG upside down and closely examine the inferior leads (II, III + aVF) for flutter waves.Narrow complex tachycardia at 150 bpm (range 130-170)? Yes -> Suspect flutter!.Handy Tips For Spotting Flutter Rapid Recognition AV block is a physiological response to rapid atrial rates and implies a normally functioning AV node.
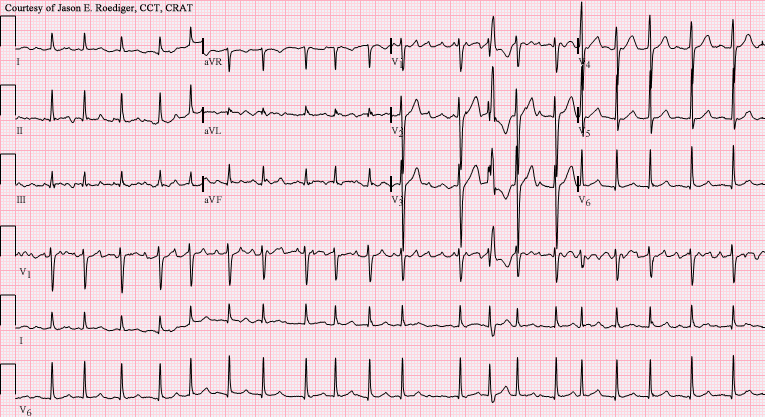
The term “AV block” in the context of atrial flutter is something of a misnomer. Atrial flutter with 1:1 conduction is associated with severe haemodynamic instability and progression to ventricular fibrillation.The administration of AV-nodal blocking agents to a patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome can precipitate this Atrial flutter with 1:1 conduction can occur due to sympathetic stimulation, or in the presence of an accessory pathway.Higher-degree blocks can occur - usually due to medications or underlying heart disease - resulting in lower rates of ventricular conduction, e.g.The most common AV ratio is 2:1, resulting in a ventricular rate of ~150 bpm Ventricular rate is determined by the AV conduction ratio (“degree of AV block”).The length of the re-entry circuit corresponds to the size of the right atrium, resulting in a fairly predictable atrial rate of around 300 bpm (range 200-400) Atrial flutter is a form of supraventricular tachycardia caused by a re-entry circuit within the right atrium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
